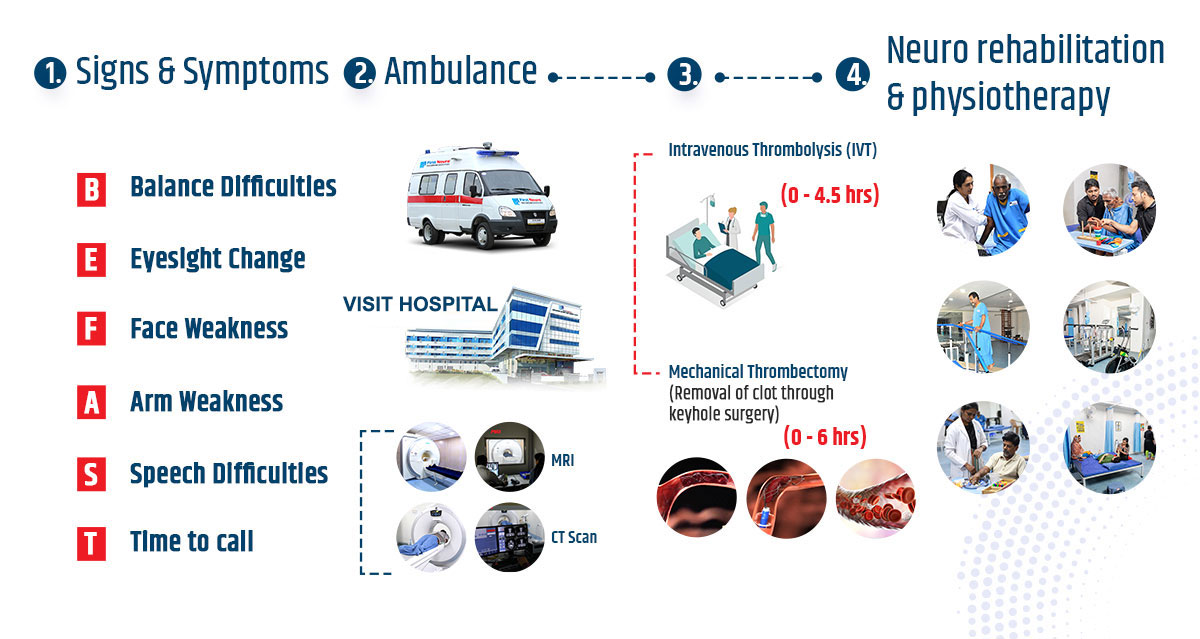
“TIME IS BRAIN”- opening a blocked artery within 4 ½ ( four and a half) hours, reverses the paralysis and prevents life time disability.
If you are experiencing these symptoms- you could be having a stroke. You should see a doctor immediately.
These symptoms can occur
if an Artery supplying blood to the brain gets blocked- this is an Ischemic Stroke Or due to an artery rupturing within the brain- this is called Brain Haemorrhage
Transient Ischemic Attack ( TIA):
Other investigations include-
STROKE REHABILITATION- is an important part of recovery after stroke.
Stroke rehabilitation includes a dynamic process of assessment, goal setting and treatment focusing on improving sensory motor deficits, functional mobility and independence in their ADL ( Activity for Daily Living )and preventing other complications. STROKE REHABILITATION- is an important part of recovery after stroke.
Those include :
The main goal of stroke rehabilitation is to help you relearn skills you lost when a stroke affected part of your brain. Stroke rehabilitation can help you regain independence and improve your quality of life.
All our specialists work as a team and help in the patient's recovering process.
TIPS FOR THE CAREGIVERS: stroke rehabilitation takes time.
Stroke Rehabilitation starts when the patient is still in hospital. Sometimes it starts as early as the next day, where our rehab team guide you to work towards making you active.
Stroke rehabilitation is a long process. One has to be very patient and dedicated and enduring while undergoing rehab. The near and dear ones of the patient can be of great help during this course. It is your patience and perseverance, love and caring attitude that will help the patient recover sooner. Encourage your loved one to be active and independent.
Epilepsy is a central nervous system (neurological) disorder in which brain activity becomes abnormal, causing seizures or periods of unusual behavior, sensations, and sometimes loss of awareness.
Anyone can develop epilepsy. Epilepsy affects both males and females of all races, ethnic backgrounds and ages.
Seizure symptoms can vary widely. Some people with epilepsy simply stare blankly for a few seconds during a seizure, while others repeatedly twitch their arms or legs. Having a single seizure doesn't mean you have epilepsy. At least two unprovoked seizures are generally required for an epilepsy diagnosis.
Treatment with medications or sometimes surgery can control seizures for the majority of people with epilepsy. Some people require lifelong treatment to control seizures, but for others, the seizures eventually go away. Some children with epilepsy may outgrow the condition with age.
Because epilepsy is caused by abnormal activity in the brain, seizures can affect any process your brain coordinates. Seizure signs and symptoms may include:
There are many types of seizures. Most seizures end in a few minutes.
These are general steps to help someone who is having any type seizure:
Here are things you can do to help someone who is having this type of seizure:
Knowing what NOT to do is important for keeping a person safe during or after a seizure.
Never do any of the following things
Seek immediate medical help if any of the following occurs:
If you experience a seizure for the first time, seek medical advice.
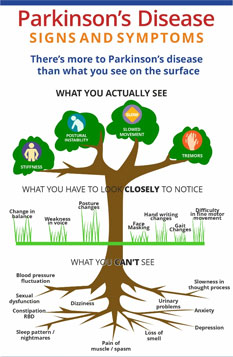
Parkinson’s disease is a neurological movement disorder. Common symptoms include tremor, slowness of movement, stiff muscles, unsteady walk and balance and coordination problems. There is no cure for the disease. Most patients can maintain a good quality of life with medications. In some patients, surgery can help improve symptoms.
Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease:
What you can see Easily : Tremors, Slowness, Stiffness, Posture changes
What you have to closely look to notice : Handwriting changes, Low voice, Masking faces, fine skill activities difficulties.
What you cannot see, but needs to be asked for : Loss of smell, Muscle pain, Urinary problems, constipation, Anxiety, depression, slowing in thought process, Sleep disturbances (Nightmares, insomnia, RBD, RLS..), Sexual dysfunction, blood pressure changes
Parkinson’s disease is a nervous system disease that affects your ability to control movement. The disease usually starts out slowly and worsens over time. If you have Parkinson’s disease, you may shake, have muscle stiffness, and have trouble walking and maintaining your balance and coordination. As the disease worsens, you may have trouble talking, sleeping, have mental and memory problems, experience behavioral changes and have other symptoms.
Scientists have discovered gene mutations that are associated with Parkinson’s disease. There is some belief that some cases of early-onset Parkinson’s disease – disease starting before age 50 – may be inherited. Scientists identified a gene mutation in people with Parkinson’s disease whose brains contain Lewy bodies, which are clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to understand the function of this protein and its relationship to genetic mutations that are sometimes seen in Parkinson’s disease and in people with a type of dementia called Lewy body dementia. Several other gene mutations have been found to play a role in Parkinson’s disease. Mutations in these genes cause abnormal cell functioning, which affects the nerve cells’ ability to release dopamine and causes nerve cell death. Researchers are still trying to discover what causes these genes to mutate in order to understand how gene mutations influence the development of Parkinson’s disease. Scientists think that about 10% to 15% of person’s with Parkinson’s disease may have a genetic mutation that predisposes them to development of the disease. There are also environmental factors involved that are not fully understood.
Symptoms of Parkinson’s disease and the rate of decline vary widely from person to person. The most common symptoms include:
Each person with Parkinson’s disease experiences symptoms in in their own unique way. Not everyone experiences all symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. You may not experience symptoms in the same order as others. Some people may have mild symptoms; others may have intense symptoms. How quickly symptoms worsen also varies from individual to individual and is difficult to impossible to predict at the outset. In general, the disease progresses from early stage to mid-stage to mid-late-stage to advanced stage. This is what typically occurs during each of these stages:
Vertigo is a sensation of feeling off balance. If you have these dizzy spells, you might feel like you are spinning or that the world around you is spinning.
Vertigo is often caused by an inner ear problem. Some of the most common causes include:
BPPV these initials stand for Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo.
BPPV occurs when tiny calcium particles (canaliths) are dislodged from their normal location and collect in the inner ear. The inner ear sends signals to the brain about head and body movements relative to gravity. It helps you keep your balance.
BPPV can occur for no known reason and may be associated with age.
Meniere's disease. This is an inner ear disorder thought to be caused by a buildup of fluid and changing pressure in the ear. It can cause episodes of vertigo along with ringing in the ears (tinnitus) and hearing loss.
Vestibular neuritis or labyrinthitis. This is an inner ear problem usually related to infection (usually viral). The infection causes inflammation in the inner ear around nerves that are important for helping the body sense balance
Less often vertigo may be associated with:
Vertigo is often triggered by a change in the position of your head.
People with vertigo typically describe it as feeling like they are:
Other symptoms that may accompany vertigo include:
Symptoms can last a few minutes to a few hours or more and may come and go.
A headache can be a sign of stress or emotional distress, or it can result from a medical disorder, such as migraine or high blood pressure, anxiety, or depression. It can lead to other problems. People with chronic migraine headaches, for example, may find it hard to attend work or school regularly.
Headache is a very common symptom and can affect people of all ages. Severe or recurring headaches, especially those accompanied by other symptoms, may be a sign of a more serious disorder and should be treated by a doctor.
Headaches can be ,
There are two types of headaches — primary, in which the headache is the disorder itself, and secondary, in which the headache is caused by another condition, such as a brain tumor; haemorrhaging or bleeding in the brain; meningitis, an infection causing inflammation of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord; or giant cell arteritis, a disorder involving inflammation and damage to blood vessels.
Migraine is the most common type of primary headache for which people seek a doctor's care. Tension-type headache is typically less severe. Other primary headache disorders, such as cluster headache, are rarer and often very severe.
“ Headaches which cannot be ignored” and need immediate attention
Migraine is the most common type of headache. These painful, recurring headaches can last hours to days, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. Symptoms of migraine-
Triggering factors-
Cluster headaches are recurring attacks of excruciating pain on one side of the head, often behind an eye. The pain may extend to the forehead, nose, cheek, upper jaw or back of the head on the same side. The attacks often happen multiple times per day, with each attack lasting less than three hours, even without treatment. Most often, the attacks occur every day for several weeks or months and then subside for a period, though for some people the attacks can continue for months or even years.
Men have cluster headaches three to four times more often than women. Generally, this condition does not run in families.
There are two kinds of cluster headache: episodic and chronic. Those suffering from episodic cluster headaches have relatively long, pain-free remissions between headaches. Chronic cluster headache sufferers do not have long remissions. If during the past year or longer, you have had only one month or less of relief between headache attacks, you may have chronic cluster headache. About 10 percent of people with cluster headaches are considered chronic sufferers.
Investigations for cluster headache


Consultant Neurologist & Epileptologist
View More >>Consultant Neurologist
View More >>